physics_joint_friction_create
The friction joint is a bit different to all other joints in the physics simulation in that the connection created will not constrain the instances position or movement, but rather its speed and rotation. This works by taking the maximum input values for force and torque and applying those to the second fixture to bring the speed and angular momentum down to the same values as that of the first instance. So, if you have a stationary instance and a moving instance then connect them with a friction joint, the moving instance will gradually slow down until it too is stationary. If both instances were moving then the second instance will have its movement speed modified to match that of the first instance.
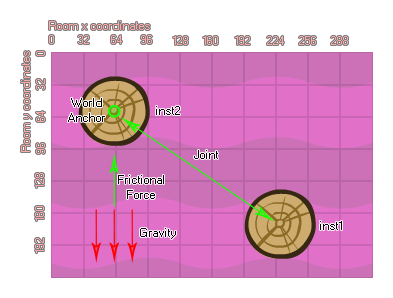 As with most other joints, you supply the instances to join together, as well as the position for the joint to be created at within the room. You then supply the maximum force and maximum torque (directional and rotational friction), and if you set the "col" value to true then the two instances can interact and collide with each other but only if they have collision events, however if it is set to false, they will not collide no matter what.
As with most other joints, you supply the instances to join together, as well as the position for the joint to be created at within the room. You then supply the maximum force and maximum torque (directional and rotational friction), and if you set the "col" value to true then the two instances can interact and collide with each other but only if they have collision events, however if it is set to false, they will not collide no matter what.
Syntax:
physics_joint_friction_create(inst1, inst2, anchor_x, anchor_y, max_force, max_torque, col)
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|
| inst1 | Object Instance | The first instance to connect with the joint |
| inst2 | Object Instance | The second instance to connect with the joint |
| anchor_x | Real | The x coordinate for the joint, within the game world |
| anchor_y | Real | The y coordinate for the joint, within the game world |
| max_force | Real | The maximum frictional force that will be applied |
| max_torque | Real | The maximum rotational force that will be applied |
| col | Boolean | Whether the two instances can collide (true) or not (false) |
Returns:
Physics Joint ID
Example:
var mainFixture, o_id;
mainFixture = physics_fixture_create();
physics_fixture_set_circle_shape(mainFixture, sprite_get_width(sprite_index) / 2);
o_id = instance_create_layer(x+300, y, "Instances", obj_Rudder);
physics_fixture_bind(mainFixture, id);
physics_fixture_bind(mainFixture, o_id);
physics_joint_friction_create(id, o_id, x, y, 10, 0.3, true);
physics_fixture_delete(mainFixture);
The above code will create a fixture then bind it to two instances, before connecting them both using a friction joint.
 As with most other joints, you supply the instances to join together, as well as the position for the joint to be created at within the room. You then supply the maximum force and maximum torque (directional and rotational friction), and if you set the "col" value to true then the two instances can interact and collide with each other but only if they have collision events, however if it is set to false, they will not collide no matter what.
As with most other joints, you supply the instances to join together, as well as the position for the joint to be created at within the room. You then supply the maximum force and maximum torque (directional and rotational friction), and if you set the "col" value to true then the two instances can interact and collide with each other but only if they have collision events, however if it is set to false, they will not collide no matter what.