To add more versatility to the audio engine, GameMaker permits you to select the falloff model that suits your game. This model will be used for all the audio functions in the game or app, and so you should make sure that the model you choose is the correct one, as each one will affect how the listener perceives the sounds you play through emitters or with the function audio_play_sound_at().
The default falloff model is audio_falloff_none, meaning there is no falloff when using emitters or positioned audio unless you change the falloff model.
When playing audio through audio_play_sound_at() or setting the falloff for an emitter, there are three arguments that you will need to set, and each one is appropriate to a specific model and will affect the way the final sound is heard by the player depending on the distance that the listener is from the source. The three arguments are:
The falloff models that are affected by these arguments are represented in GameMaker by the following constants (the table shows the exact calculations used too):
| Audio Falloff Constant | |
|---|---|
| Constant | Gain Calculation |
| audio_falloff_exponent_distance | gain = (listener_distance / reference_distance) ^ (-falloff_factor) |
| audio_falloff_exponent_distance_clamped | distance = clamp(listener_distance, reference_distance, maximum_distance) gain = (distance / reference_distance) ^ (-falloff_factor) |
| audio_falloff_exponent_distance_scaled | distance = clamp(listener_distance, reference_distance, maximum_distance) gain = ((distance / reference_distance) ^ (-falloff_factor)) * (((maximum_distance - distance) / (maximum_distance - reference_distance)) ^ (distance / maximum_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_inverse_distance | gain = reference_distance / (reference_distance + falloff_factor * (listener_distance - reference_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_inverse_distance_clamped | distance = clamp(listener_distance, reference_distance, maximum_distance) gain = reference_distance / (reference_distance + falloff_factor * (distance - reference_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_inverse_distance_scaled | distance = clamp(listener_distance, reference_distance, maximum_distance) gain = (reference_distance / (reference_distance + falloff_factor * (distance - reference_distance))) * (((maximum_distance - distance) / (maximum_distance - reference_distance)) ^ (distance / maximum_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_linear_distance | distance = min(distance, maximum_distance) gain = (1 - falloff_factor * (distance - reference_distance) / (maximum_distance - reference_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_linear_distance_clamped | distance = clamp(listener_distance, reference_distance, maximum_distance) gain = (1 - falloff_factor * (distance - reference_distance) / (maximum_distance - reference_distance)) |
| audio_falloff_none | gain = 1 |
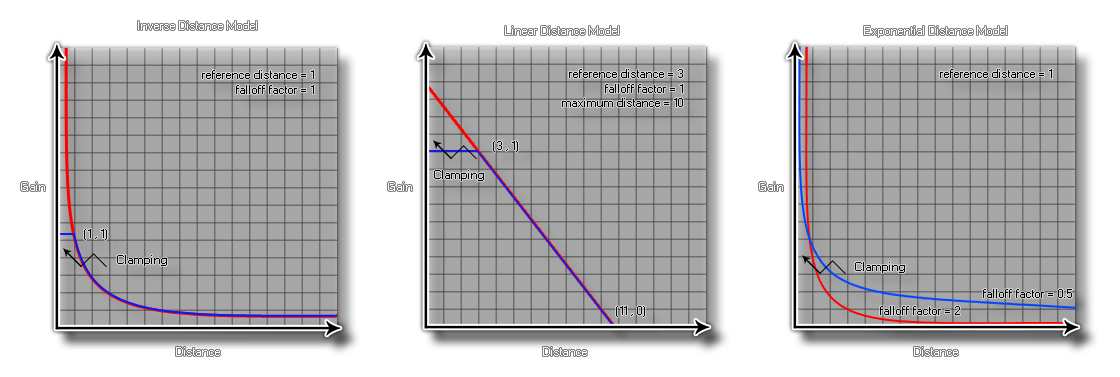
The "_scaled" models are scaled in such a way that sounds are guaranteed to fall off entirely by the maximum distance.
The following graphs are visual representations of how some of the above constants work and affect the sound being played:

In HTML5 the _clamped and _scaled variants are unsupported, as Web Audio doesn't support them. If you set the falloff model to one of these constants on HTML5, GameMaker will internally use the nearest available model as follows:
This change only happens internally, the falloff model value remains the one that you passed to the function.
audio_falloff_set_model(model);
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| model | Audio Falloff Constant | The constant used to set the falloff model. |
N/A
audio_falloff_set_model(audio_falloff_exponent_distance_clamped);
audio_play_sound_at(snd_Waterfall, x, y, 0, 100, 300, 1, true, 1);
The above code sets the falloff model and then plays the sound indexed in the variable "snd_Waterfall", which will be looped at its room position, with a fall-off reference of 100, a falloff distance of 300, a falloff factor of 1 and a low priority.